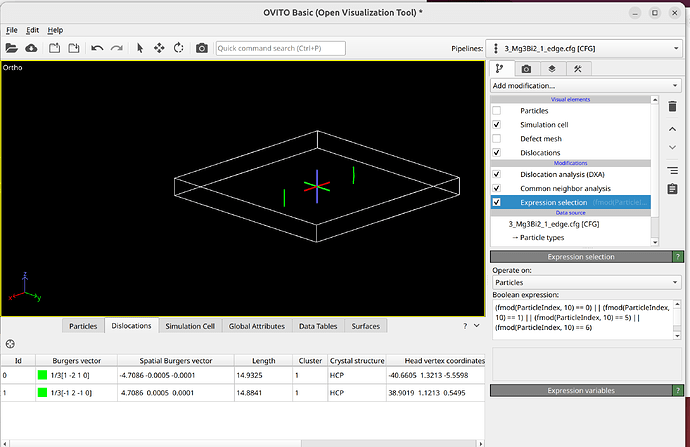
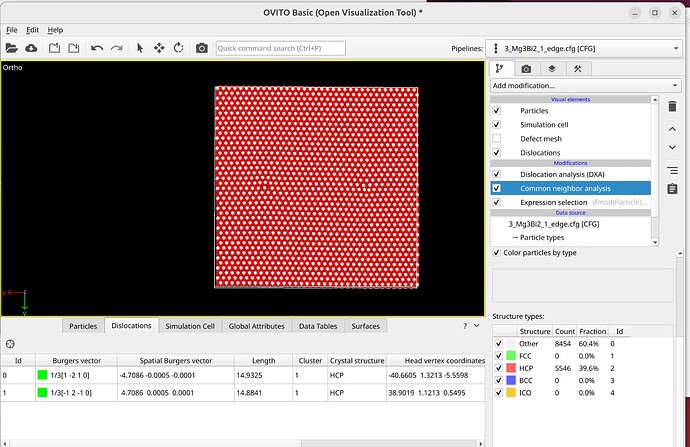
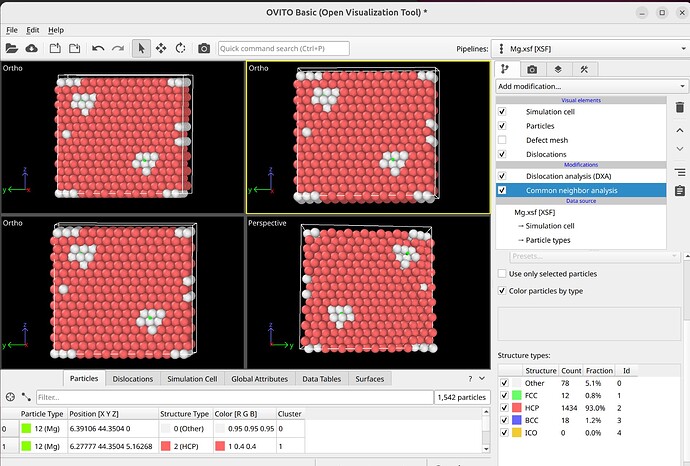
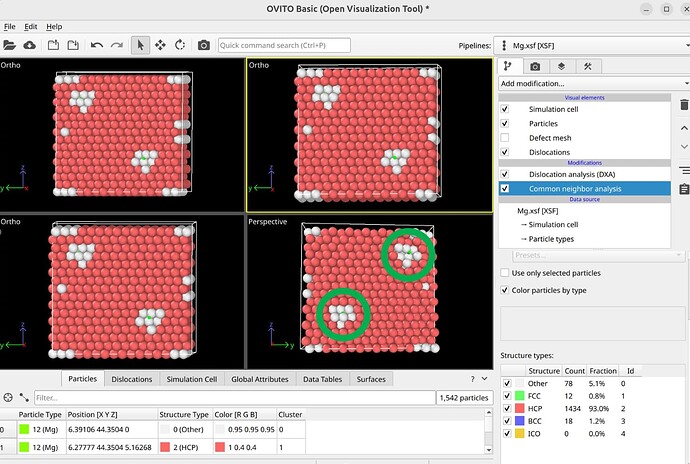
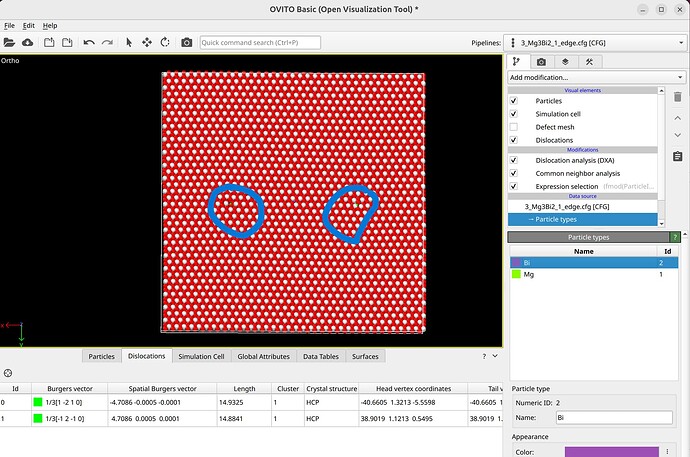
To select dislocation core atoms, you can use the “mark dislocation core atoms” setting in DXA. This will mark atoms that are part of the defective region identified as the dislocation core. You can select them using the expression selection modifier with the expression: Dislocation>=0. Note that this will only select atoms that are part of the existing selection used as input into DXA. Therefore, you have to use the expand selection modifier to select other atoms inside the unit cell that were not selected previously.
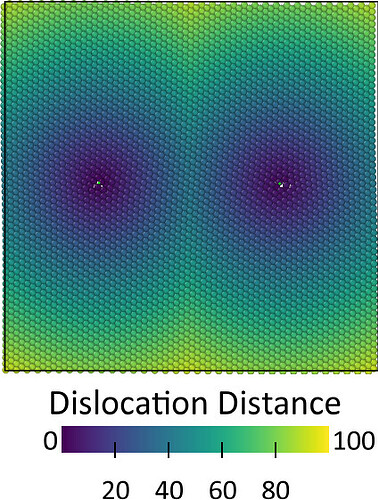
Alternatively, you can compute the distance for all atoms to the dislocation line using this code:
"""
Copyright (c) 2025 Daniel Utt
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of
this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in
the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to
use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of
the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so,
subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR
COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER
IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN
CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
"""
from ovito.data import DataCollection
from ovito.pipeline import ModifierInterface
import numpy as np
class DislocationDistanceModifier(ModifierInterface):
@staticmethod
def distance_points_to_segment_3d(points, seg_start, seg_end):
"""
Calculate the minimum distance from multiple points to a line segment in 3D.
Args:
points: array-like of shape (n, 3) - array of points [(x1, y1, z1), (x2, y2, z2), ...]
seg_start: tuple/array (x, y, z) - start point of line segment
seg_end: tuple/array (x, y, z) - end point of line segment
Returns:
numpy array: distances from each point to the line segment
"""
points = np.array(points)
seg_start = np.array(seg_start)
seg_end = np.array(seg_end)
# Vector from seg_start to seg_end
segment_vec = seg_end - seg_start
# Handle degenerate case where segment is a point
segment_length_sq = np.dot(segment_vec, segment_vec)
if segment_length_sq == 0:
return np.linalg.norm(points - seg_start, axis=1)
# Calculate parameter t for each point
# t represents where the projection falls on the line
point_vecs = points - seg_start
t = np.dot(point_vecs, segment_vec) / segment_length_sq
# Clamp t to [0, 1] to stay within the segment
t = np.clip(t, 0, 1)
# Find the closest point on the segment for each input point
closest_points = seg_start + t[:, np.newaxis] * segment_vec
# Calculate distances
distances = np.linalg.norm(points - closest_points, axis=1)
return distances
def modify(self, data: DataCollection, *, frame: int, **kwargs):
# Get the positions of all particles
positions = np.asarray(data.particles.positions)
# Pre-allocate the array for storing the minimum distances
dislocation_distances = np.ones(positions.shape[0]) * np.inf
# Loop over dislocations
for segment in data.dislocations.segments:
# Loop over all dislocation line segments
for i in range(1, len(segment.points)):
# Compute the minimum distance from each particle to the current line segment
distances = self.distance_points_to_segment_3d(
positions, segment.points[i - 1], segment.points[i]
)
# Update the minimum distance for each particle
dislocation_distances = np.minimum(dislocation_distances, distances)
yield i / len(segment.points)
# Store distances in data object
data.particles_.create_property(
"Dislocation Distance", data=dislocation_distances
)
Subsequently, the expression selection modifier can be used to select all atoms within a given distance from the dislocation as core atoms.